NASA’s exploration of Mars has a long history, beginning in the 1960s with a series of ambitious, albeit initially unsuccessful, missions. Over the decades, NASA has refined its approach and technology, leading to significant achievements and insights about the Red Planet. One of the most remarkable milestones in this journey was the Phoenix mission, which provided some of the most valuable data in the history of Mars exploration.
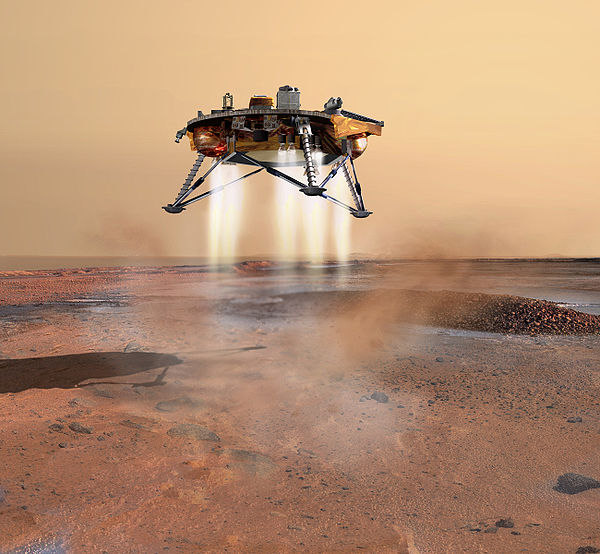

Phoenix Mission Overview:
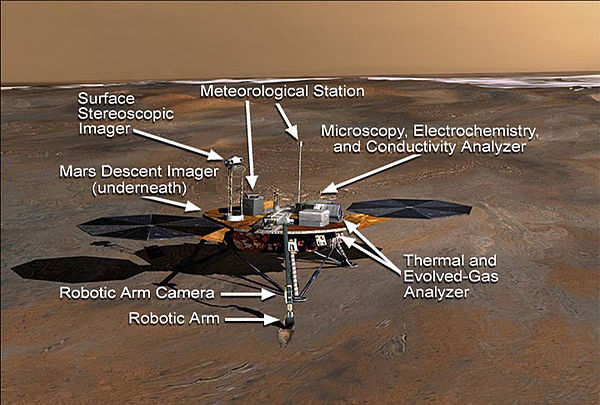
The Phoenix mission was a robotic spacecraft mission that aimed to conduct scientific exploration in the Martian polar region. It marked NASA’s first successful landing in this area, making history by touching down on Mars on May 25, 2008, after being launched from Earth on August 4, 2007. The mission’s objective was to study the Martian arctic’s soil and atmosphere and to search for environments that could support microbial life.
Key Achievements:
- Successful Polar Landing: The Phoenix mission’s landing site in the northern plains of Mars provided a unique opportunity to study the Martian arctic, a region previously unexplored by landed missions.
- Soil Analysis: One of Phoenix’s most significant findings was the chemical analysis of Martian soil. The data revealed that the soil was slightly alkaline, containing nutrients such as magnesium, sodium, potassium, and chlorine—elements that are essential for plant growth on Earth. This discovery suggested that the Martian environment might be more hospitable than previously thought.
- Water Research: Phoenix contributed substantially to our understanding of water on Mars. The lander detected the presence of water-ice just beneath the Martian surface, supporting the hypothesis that water exists in some form on Mars and has shaped its geological history.
Mission Conclusion:
Despite its groundbreaking achievements, the Phoenix mission was relatively short-lived. After five months of successful data gathering and exploration, NASA declared the mission concluded on November 10, 2008. The decision was made after engineers could no longer establish contact with the spacecraft, likely due to the onset of Martian winter and the reduced solar power available to the lander.
Cost and Legacy:
The Phoenix mission had a total cost of approximately ₹2370 crore. Its legacy continues to impact current and future Mars exploration missions, providing essential data that has helped refine our understanding of the Martian environment and its potential to support life. Phoenix demonstrated that Mars has many Earth-like qualities and that continued exploration could reveal even more about our neighboring planet.
Overall, the Phoenix mission stands as a testament to human curiosity and perseverance in the quest to explore and understand the cosmos.
#Hindi
नासा की मंगल ग्रह की खोज का एक लंबा इतिहास है, जो 1960 के दशक में कुछ साहसी मगर शुरू में असफल मिशनों के साथ शुरू हुआ था। समय के साथ, नासा ने अपनी तकनीक और तरीकों में सुधार किया, जिससे लाल ग्रह के बारे में महत्वपूर्ण उपलब्धियां और अंतर्दृष्टियाँ मिलीं। इस यात्रा में फीनिक्स मिशन एक महत्वपूर्ण मील का पत्थर था, जिसने मंगल की खोज के इतिहास में कुछ सबसे मूल्यवान डेटा प्रदान किए।
फीनिक्स मिशन का अवलोकन:
फीनिक्स मिशन एक रोबोटिक अंतरिक्ष यान मिशन था जिसका उद्देश्य मंगल के ध्रुवीय क्षेत्र में वैज्ञानिक अन्वेषण करना था। यह नासा की इस क्षेत्र में पहली सफल लैंडिंग थी, जिसने 25 मई, 2008 को मंगल पर सफलतापूर्वक उतर कर इतिहास बनाया। इसे 4 अगस्त, 2007 को पृथ्वी से लॉन्च किया गया था। मिशन का उद्देश्य मंगल के आर्कटिक की मिट्टी और वातावरण का अध्ययन करना और ऐसे वातावरण की खोज करना था जो सूक्ष्मजीव जीवन का समर्थन कर सकें।
मुख्य उपलब्धियाँ:
सफल ध्रुवीय लैंडिंग: फीनिक्स मिशन की लैंडिंग साइट ने मंगल के उत्तरी मैदानों में अन्वेषण के लिए एक अनूठा अवसर प्रदान किया, जो पहले किसी अभियानों द्वारा नहीं किया गया था।
मिट्टी का विश्लेषण: फीनिक्स की सबसे महत्वपूर्ण खोजों में से एक मंगल की मिट्टी का रासायनिक विश्लेषण था। डेटा से पता चला कि मिट्टी थोड़ा क्षारीय थी, जिसमें मैग्नीशियम, सोडियम, पोटैशियम और क्लोरीन जैसे पोषक तत्व थे। इस खोज से यह संकेत मिला कि मंगल का वातावरण पहले से सोचा गया की तुलना में अधिक सहयोगी हो सकता है।
पानी का अनुसंधान: फीनिक्स ने मंगल पर पानी की समझ में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया। लैंडर ने मंगल की सतह के नीचे पानी की बर्फ की उपस्थिति का पता लगाया, जिससे यह सिद्धांत मजबूत हुआ कि मंगल पर किसी न किसी रूप में पानी मौजूद है और उसने वहाँ की भूवैज्ञानिक इतिहास को आकार दिया है।
मिशन का समापन:
अपनी क्रांतिकारी उपलब्धियों के बावजूद, फीनिक्स मिशन अपेक्षाकृत अल्पकालिक था। पाँच महीने की सफल डेटा संग्रहण और अन्वेषण के बाद, नासा ने 10 नवंबर, 2008 को मिशन के समाप्त होने की घोषणा की। यह निर्णय तब लिया गया जब इंजीनियरों को अंतरिक्ष यान से संपर्क स्थापित करने में कठिनाई हुई, संभवतः मंगल के सर्दी के कारण और लैंडर को उपलब्ध सौर ऊर्जा में कमी के कारण।
लागत और विरासत:
फीनिक्स मिशन की कुल लागत लगभग ₹2370 करोड़ थी। इसकी विरासत मौजूदा और भविष्य के मंगल अन्वेषण मिशनों को प्रभावित करती है, उसने मंगल के वातावरण और जीवन के समर्थन की संभावनाओं को समझने में महत्वपूर्ण डेटा प्रदान किया है। फीनिक्स ने दिखाया कि मंगल में कई पृथ्वी जैसी विशेषताएँ हैं और निरंतर अन्वेषण से हमारे पड़ोसी ग्रह के बारे में और भी अधिक जानकारी मिल सकती है।
संपूर्ण रूप से, फीनिक्स मिशन मानव जिज्ञासा और ब्रह्मांड को समझने की खोज में दृढ़ता का प्रमाण है।
NASA’s exploration of Mars has a long history, beginning in the 1960s with a series of ambitious, albeit initially unsuccessful, missions. Over the decades, NASA has refined its approach and technology, leading to significant achievements and insights about the Red Planet. One of the most remarkable milestones in this journey was the Phoenix mission, which provided some of the most valuable data in the history of Mars exploration.
Phoenix Mission Overview:
The Phoenix mission was a robotic spacecraft mission that aimed to conduct scientific exploration in the Martian polar region. It marked NASA’s first successful landing in this area, making history by touching down on Mars on May 25, 2008, after being launched from Earth on August 4, 2007. The mission’s objective was to study the Martian arctic’s soil and atmosphere and to search for environments that could support microbial life.
Key Achievements:
Mission Conclusion:
Despite its groundbreaking achievements, the Phoenix mission was relatively short-lived. After five months of successful data gathering and exploration, NASA declared the mission concluded on November 10, 2008. The decision was made after engineers could no longer establish contact with the spacecraft, likely due to the onset of Martian winter and the reduced solar power available to the lander.
Cost and Legacy:
The Phoenix mission had a total cost of approximately ₹2370 crore. Its legacy continues to impact current and future Mars exploration missions, providing essential data that has helped refine our understanding of the Martian environment and its potential to support life. Phoenix demonstrated that Mars has many Earth-like qualities and that continued exploration could reveal even more about our neighboring planet.
Overall, the Phoenix mission stands as a testament to human curiosity and perseverance in the quest to explore and understand the cosmos.
#Hindi
नासा की मंगल ग्रह की खोज का एक लंबा इतिहास है, जो 1960 के दशक में कुछ साहसी मगर शुरू में असफल मिशनों के साथ शुरू हुआ था। समय के साथ, नासा ने अपनी तकनीक और तरीकों में सुधार किया, जिससे लाल ग्रह के बारे में महत्वपूर्ण उपलब्धियां और अंतर्दृष्टियाँ मिलीं। इस यात्रा में फीनिक्स मिशन एक महत्वपूर्ण मील का पत्थर था, जिसने मंगल की खोज के इतिहास में कुछ सबसे मूल्यवान डेटा प्रदान किए।
फीनिक्स मिशन का अवलोकन:
फीनिक्स मिशन एक रोबोटिक अंतरिक्ष यान मिशन था जिसका उद्देश्य मंगल के ध्रुवीय क्षेत्र में वैज्ञानिक अन्वेषण करना था। यह नासा की इस क्षेत्र में पहली सफल लैंडिंग थी, जिसने 25 मई, 2008 को मंगल पर सफलतापूर्वक उतर कर इतिहास बनाया। इसे 4 अगस्त, 2007 को पृथ्वी से लॉन्च किया गया था। मिशन का उद्देश्य मंगल के आर्कटिक की मिट्टी और वातावरण का अध्ययन करना और ऐसे वातावरण की खोज करना था जो सूक्ष्मजीव जीवन का समर्थन कर सकें।
मुख्य उपलब्धियाँ:
सफल ध्रुवीय लैंडिंग: फीनिक्स मिशन की लैंडिंग साइट ने मंगल के उत्तरी मैदानों में अन्वेषण के लिए एक अनूठा अवसर प्रदान किया, जो पहले किसी अभियानों द्वारा नहीं किया गया था।
मिट्टी का विश्लेषण: फीनिक्स की सबसे महत्वपूर्ण खोजों में से एक मंगल की मिट्टी का रासायनिक विश्लेषण था। डेटा से पता चला कि मिट्टी थोड़ा क्षारीय थी, जिसमें मैग्नीशियम, सोडियम, पोटैशियम और क्लोरीन जैसे पोषक तत्व थे। इस खोज से यह संकेत मिला कि मंगल का वातावरण पहले से सोचा गया की तुलना में अधिक सहयोगी हो सकता है।
पानी का अनुसंधान: फीनिक्स ने मंगल पर पानी की समझ में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया। लैंडर ने मंगल की सतह के नीचे पानी की बर्फ की उपस्थिति का पता लगाया, जिससे यह सिद्धांत मजबूत हुआ कि मंगल पर किसी न किसी रूप में पानी मौजूद है और उसने वहाँ की भूवैज्ञानिक इतिहास को आकार दिया है।
मिशन का समापन:
अपनी क्रांतिकारी उपलब्धियों के बावजूद, फीनिक्स मिशन अपेक्षाकृत अल्पकालिक था। पाँच महीने की सफल डेटा संग्रहण और अन्वेषण के बाद, नासा ने 10 नवंबर, 2008 को मिशन के समाप्त होने की घोषणा की। यह निर्णय तब लिया गया जब इंजीनियरों को अंतरिक्ष यान से संपर्क स्थापित करने में कठिनाई हुई, संभवतः मंगल के सर्दी के कारण और लैंडर को उपलब्ध सौर ऊर्जा में कमी के कारण।
लागत और विरासत:
फीनिक्स मिशन की कुल लागत लगभग ₹2370 करोड़ थी। इसकी विरासत मौजूदा और भविष्य के मंगल अन्वेषण मिशनों को प्रभावित करती है, उसने मंगल के वातावरण और जीवन के समर्थन की संभावनाओं को समझने में महत्वपूर्ण डेटा प्रदान किया है। फीनिक्स ने दिखाया कि मंगल में कई पृथ्वी जैसी विशेषताएँ हैं और निरंतर अन्वेषण से हमारे पड़ोसी ग्रह के बारे में और भी अधिक जानकारी मिल सकती है।
संपूर्ण रूप से, फीनिक्स मिशन मानव जिज्ञासा और ब्रह्मांड को समझने की खोज में दृढ़ता का प्रमाण है।
Share this: